Safe Internet - Update your Browser
Can you remember when the last time you checked whether your internet browser had the latest updates installed?
As announced by Google last week, the Chrome browser received an update which included fixes to seven (7) vulnerabilities, of which four are rated as high severity and the CISA urges consumers to update their browser.
Researchers from external organizations reported three of these vulnerabilities via Google's bug bounty program. It has been decided by Google that it will not release specific bug information until most users have updated their Chrome browser to the latest version (102.0.5005.115).
Follow these steps to verify the version of Chrome you have installed:
To access the menu, click on the kebab menu (the three dots in the upper right-hand corner of your Chrome browser).
2. Navigate to the “Help” menu, followed by “About Google Chrome.”
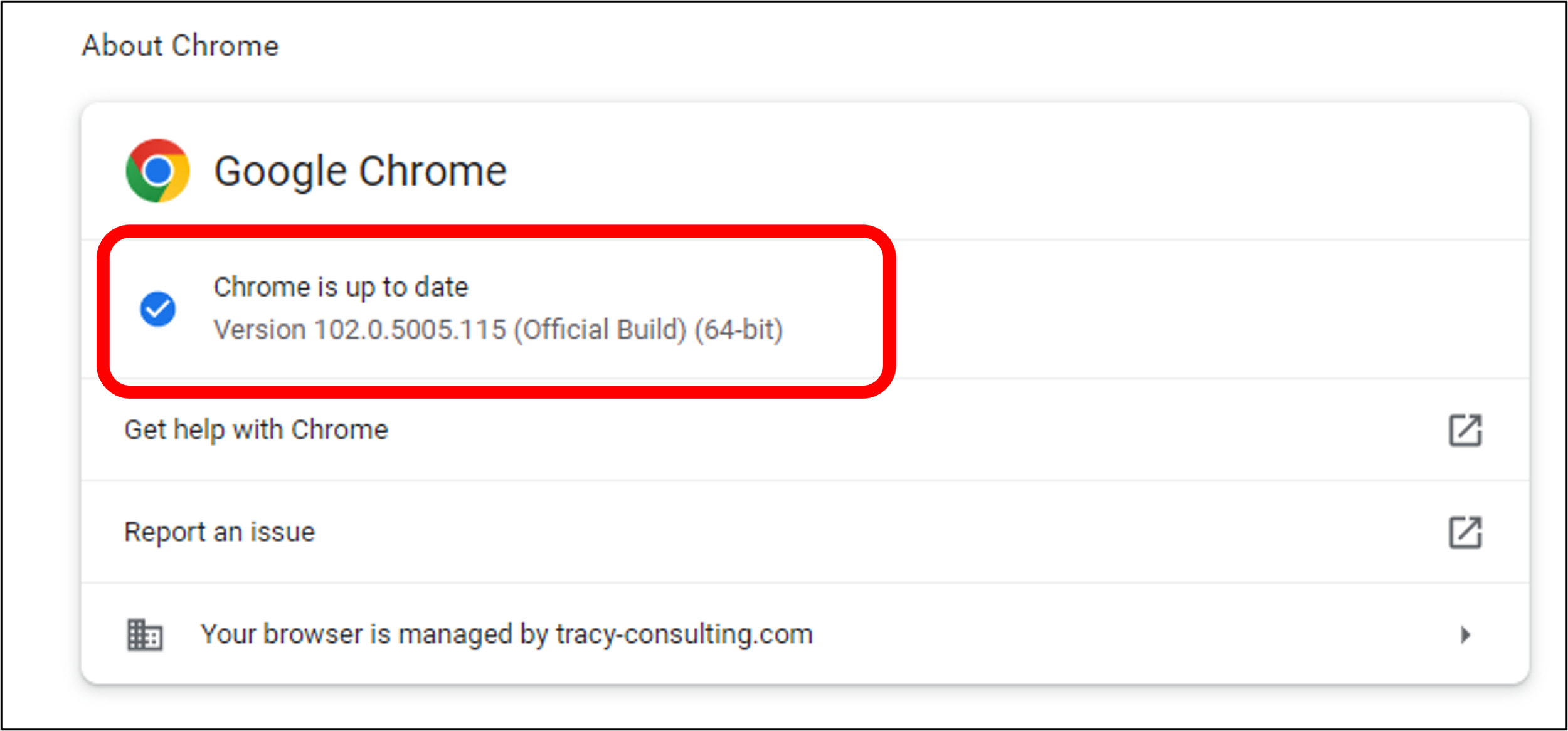
3. The Chrome browser information will be displayed in a new tab. You will find the version number in the first section, under “About Chrome.”
Why is so important to update?
Keeping your browser updated will ensure that you have the latest security patches. The cybercriminal will utilize the vulnerabilities in browsers to gain access to your system and to sensitive information such as your passwords, which can be used to hack into your various accounts. Let's examine four vulnerabilities in Chrome..
One of the vulnerabilities, for which Google rewarded the researcher $10,000, is a use after free issue in the WebGPU API, which allows computation and rendering on GPUs. "Use after free" attacks are those in which the attacker references memory after it has been freed, resulting in a program crash, unexpected values, or code execution. As for the vulnerability (CVE-2022-2007), it is fairly easy to exploit, can be done remotely (that is, no physical proximity to the affected system is needed) and will have a significant impact on all three aspects of cybersecurity (containment, integrity, and availability). The vulnerability database VulDB notes “No form of authentication is needed for exploitationhowever, it does require that the victim is doing some kind of user interaction.”
In the second high-severity vulnerability (CVE-2022-2008), a flaw is found in the WebGL API for rendering 2D and 3D graphics. This flaw was found by two researchers from a Vietnamese company named VinCSS Internet Security Services. This can also be carried out remotely with no authentication necessary, however it does require some user interaction. In case of a memory out-of-bounds read, a malicious attacker may be able to read sensitive information from other locations or cause a crash. Google hasn't determined the reward for disclosing this vulnerability as of this writing.
Another out-of-bound read vulnerability (CVE-2022-2008) affects rendering webpage content or composting content. A security researcher working with Google Project Zero found this vulnerability. Similarly to the previous two flaws, this one also affects confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the system.
The final high-severity vulnerability (CVE-2022-2011) was reported by an external researcher as a “use after free” issue. An exploitable vulnerability exists in the ANGLE engine, which translates OpenGL ES API calls into one of the hardware-supported APIs available for that particular platform in order to run WebGL and OpenGL ES content on multiple operating systems. As described by VulDB, the memory corruption has nearly the same impact as the three other vulnerabilities.
All of the vulnerabilities point to the possibility of an attacker being able to remotely access your system, view sensitive information, or crash your system at will. In the post-pandemic world, Internet connectivity allows us to stay in touch with friends, stay informed, and stay mobile, but it can also expose us to cybercriminals looking for easy ways to increase their profits.
I recommend you stop reading this article and check your Chrome version immediately. If you find that your Chrome version needs updating, please do so immediately. If you do not use Chrome, you may wish to examine the security notices provided by your browser to determine whether any urgent updates are required. I have included a list of the most common browsers below, but if yours is not listed, simply search “security advisories" along with the name of your browser.
Firefox: https://www.mozilla.org/en-US/security/known-vulnerabilities/firefox/
Microsoft Edge: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/deployedge/microsoft-edge-relnotes-security
All Apple Products: https://support.apple.com/en-us/HT201222
Opera: https://security.opera.com/en/advisories/
Abbreviations/Terminology used in this post:
API: Application programming interfaces; enables companies to open up their applications’ data and functionality to external third-party developers, business partners, and internal departments within their companies. This allows services and products to communicate with each other and leverage each other’s data and functionality through a documented interface
CISA: Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency
Composting: Since the parts of the page were drawn into potentially multiple layers they need to be drawn to the screen in the correct order so that the page renders correctly. This is especially important for elements that overlap another, since a mistake could result in one element appearing over the top of another incorrectly.
ES: embedded systems; microprocessor-based computer hardware system with software that is designed to perform a dedicated function, either as an independent system or as a part of a large system
GL: Graphics Layer; A Graphics Layer contains one or more client-side Graphics. Each graphic in the Graphics Layer is rendered in a LayerView inside either a SceneView or a MapView. The graphics contain discrete vector geometries that represent real-world phenomena.
GPU: Graphics Processing Unit; Designed for parallel processing, the GPU is used in a wide range of applications, including graphics and video rendering